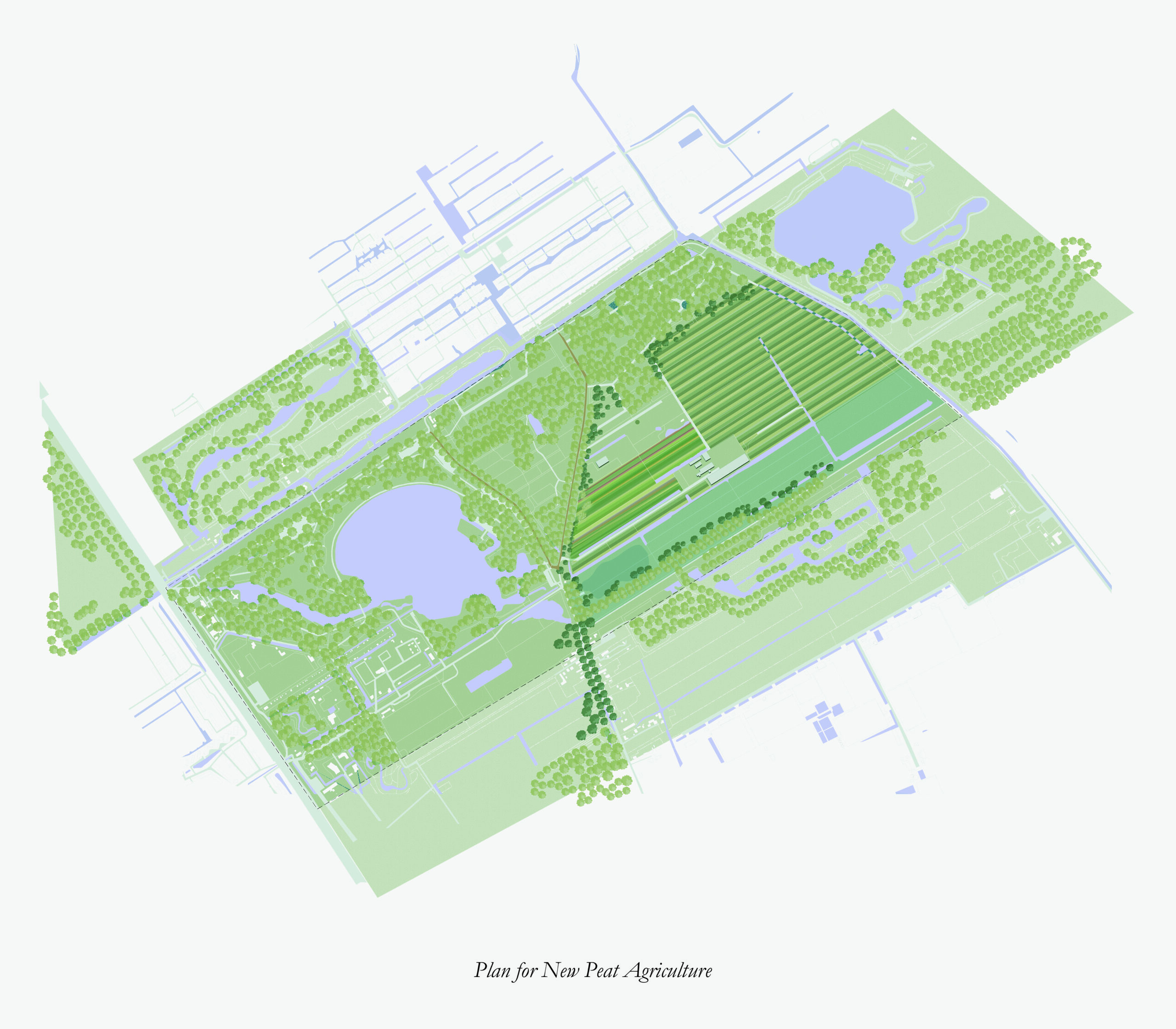
The Landscape Vision
(Co)Designing with the Farmer
The second phase involved co-designing a future landscape plan with the farmer-owner of this area. How will climate change impact this agricultural area and its flora and fauna? What interventions can we plan for the short and long term?
The Biodiversity Vision
From a landscape perspective, the future vision outlines the development plan for the Delftse Hout and Biesland Polder area over the next five years. Surrounded by Delft, Pijnacker, and Nootdorp, this core green space holds significant ecological, recreational, and economic value for the neighboring urban regions.
The vision’s principles prioritize ecological function, sustainable development, and minimal human intervention. After studying the area’s hydrology, soil, agriculture, flora, and fauna, the team anticipated potential climate change challenges the region might face and developed six strategies to address them. While each strategy focuses on different aspects, they tackle three main concerns: biodiversity, carbon storage, spatial quality, and multifunctionality. The vision’s master plan illustrates how these strategies will be applied.
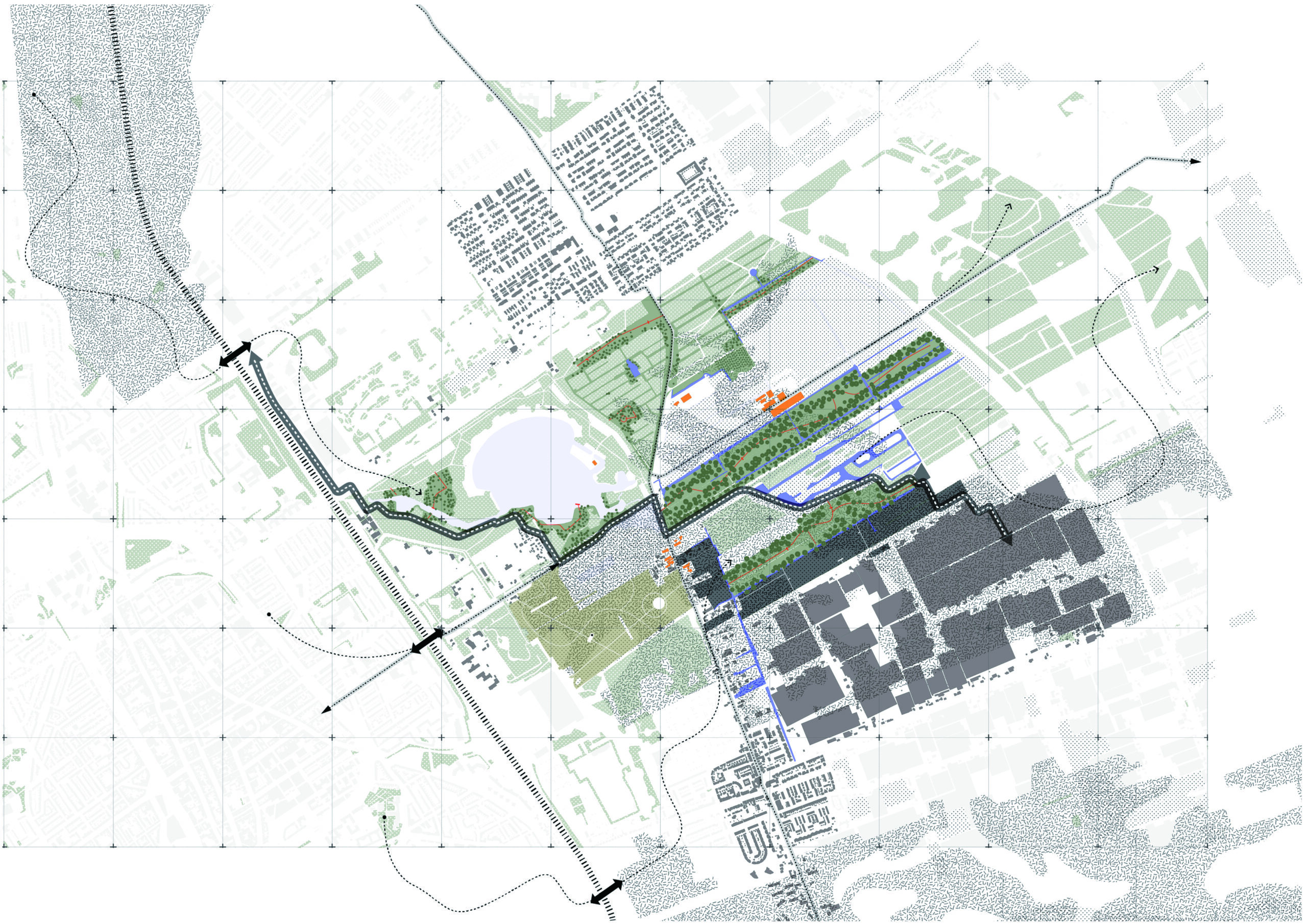
After studying the area’s hydrology, soil, agriculture, flora, and fauna, the team anticipated potential climate change challenges the region might face and developed six strategies to address them.
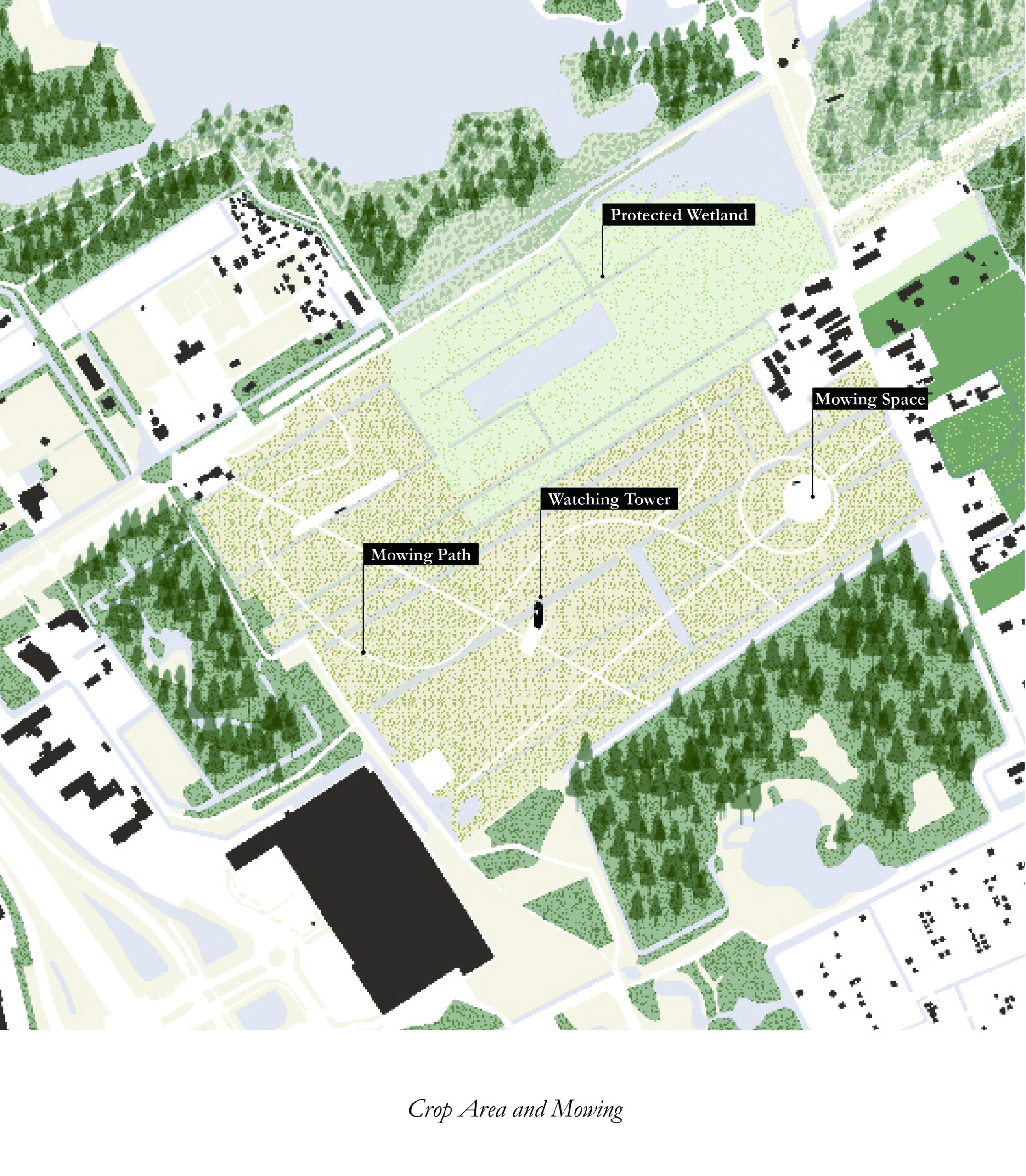
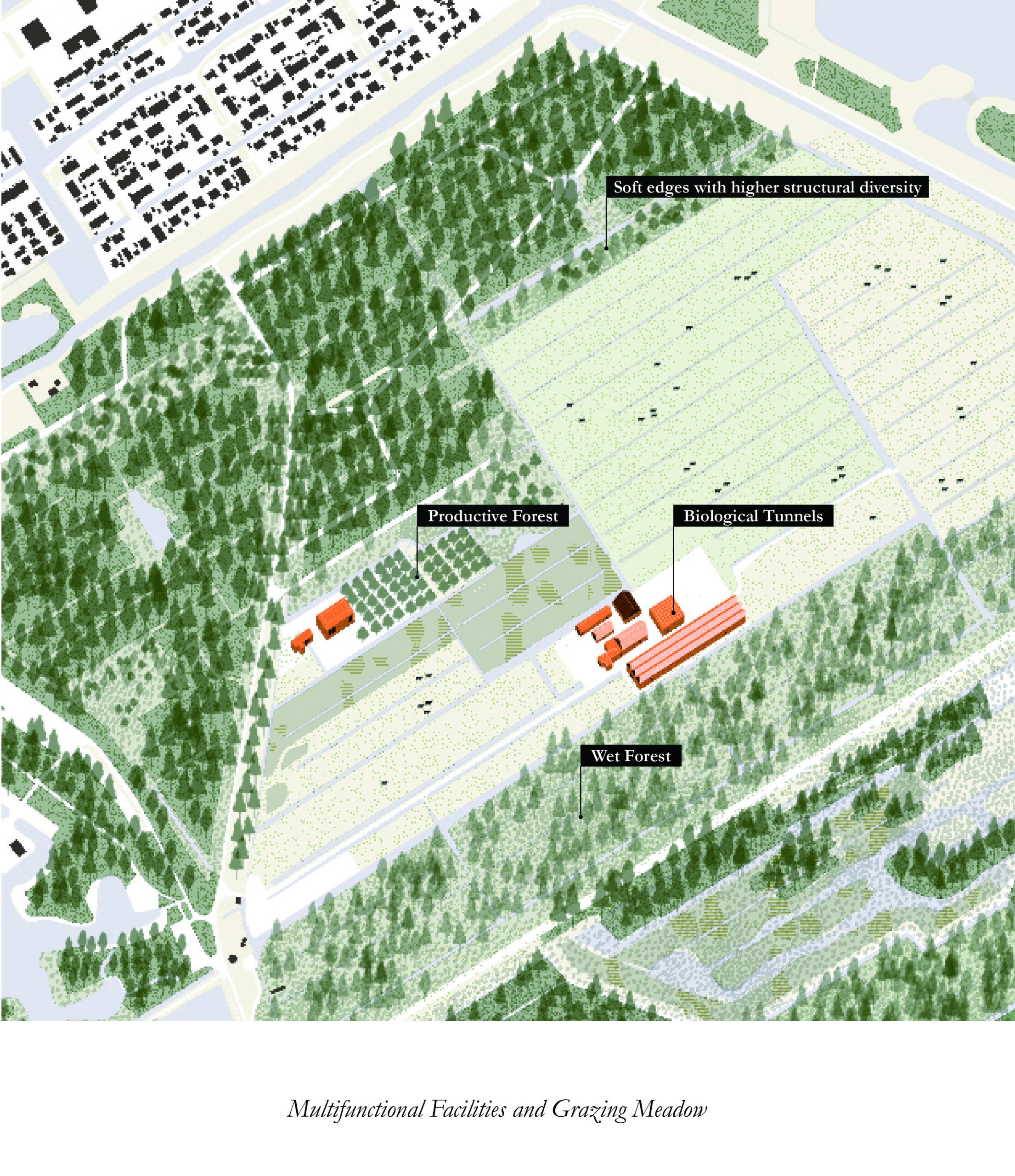
The Peat Vision
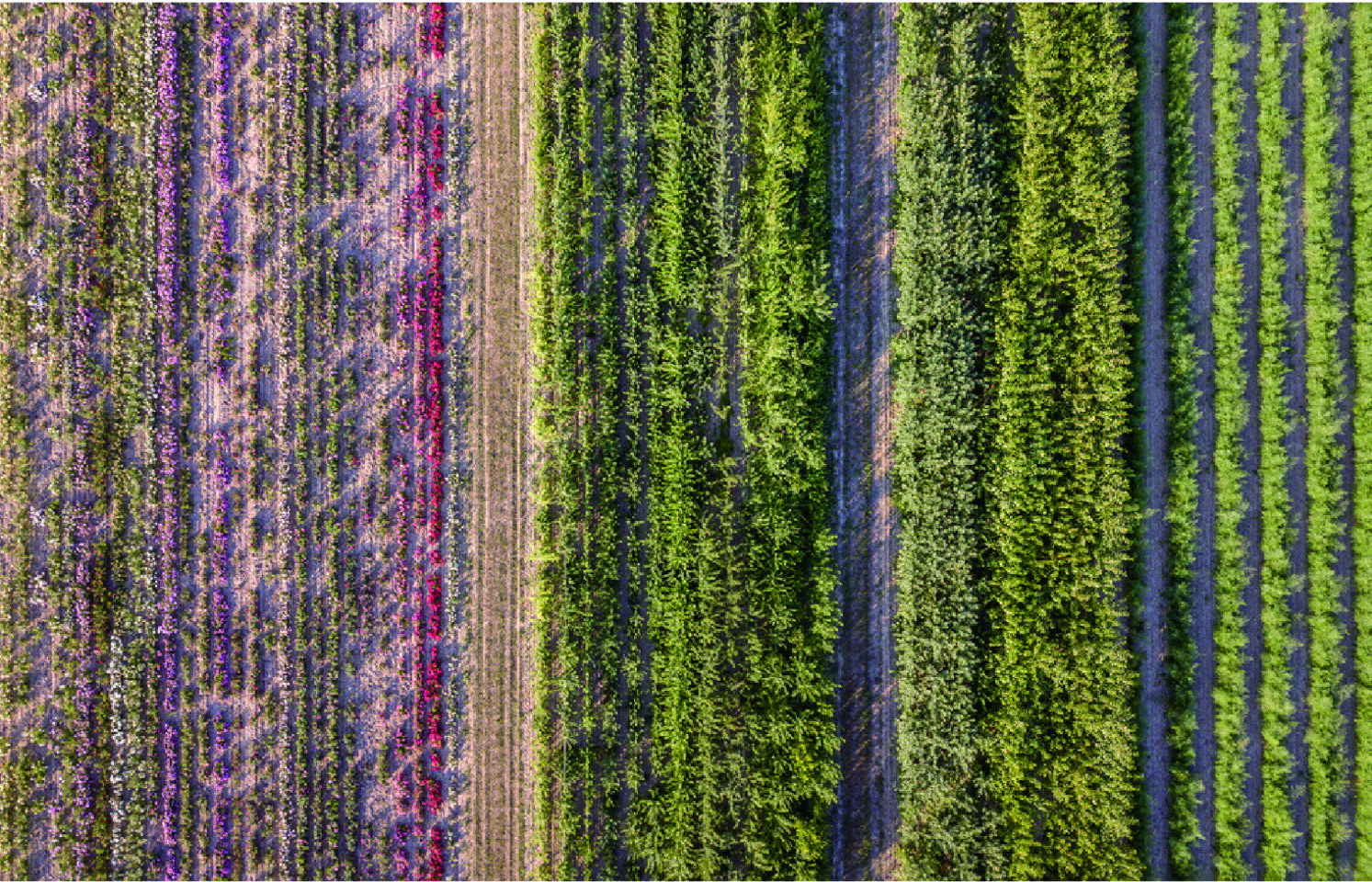
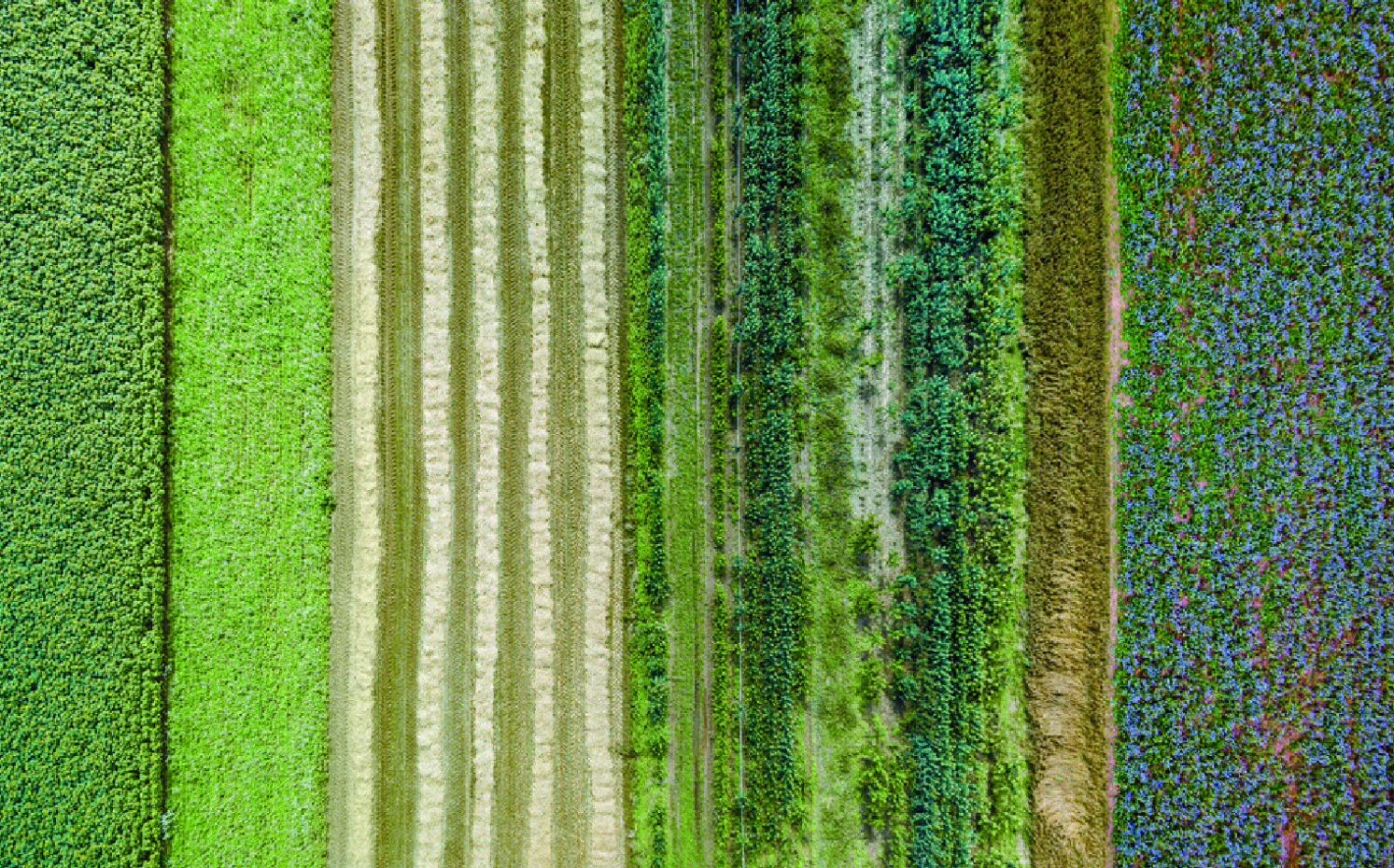
This vision outlines a comprehensive strategy for transforming agricultural practices and enhancing environmental sustainability in Delftse Hout and Stiltegoed through three key approaches: improving soil health, boosting biodiversity, and generating economic benefits.
Agricultural diversification includes strip cropping and paludiculture, which mitigate the effects of climate change, such as rising water levels and droughts, while reducing greenhouse gas emissions like CO2 and methane. This approach supports water purification, prevents soil degradation, and preserves diverse plant and animal species. Growing high-value crops such as reeds and medicinal plants presents economic opportunities. Agroforestry and animal grazing enhance recreational activities, inviting visitors to picnic among the meadow landscapes. Expanding children’s facilities increases recreational options.